Introduce
Bubble Sort is the simplest sorting algorithm that works by repeatedly swapping the adjacent elements if they are in wrong order.
Example:
First Pass:
- ( 5 1 4 2 8 ) –> ( 1 5 4 2 8 ), Here, algorithm compares the first two elements, and swaps since 5 > 1.
- ( 1 5 4 2 8 ) –> ( 1 4 5 2 8 ), Swap since 5 > 4
- ( 1 4 5 2 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 ), Swap since 5 > 2
- ( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 ), Now, since these elements are already in order (8 > 5), algorithm does not swap them.
Second Pass:
- ( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 )
- ( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 ), Swap since 4 > 2
- ( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
- ( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 ) Now, the array is already sorted, but our algorithm does not know if it is completed. The algorithm needs one whole pass without any swap to know it is sorted.
Third Pass:
- ( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
- ( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
- ( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
- ( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
Illustration
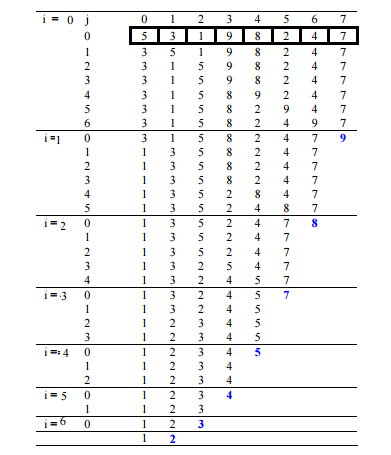
Exampls
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int *xp, int *yp)
{
int temp = *xp;
*xp = *yp;
*yp = temp;
}
// A function to implement bubble sort
void bubbleSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n-1; i++)
// Last i elements are already in place
for (j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++)
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1])
swap(&arr[j], &arr[j+1]);
}
/* Function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
bubbleSort(arr, n);
cout<<"Sorted array: "<<endl;
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
Java
// Optimized java implementation
// of Bubble sort
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
// An optimized version of Bubble Sort
static void bubbleSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, j, temp;
boolean swapped;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
swapped = false;
for (j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
{
// swap arr[j] and arr[j+1]
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
swapped = true;
}
}
// IF no two elements were
// swapped by inner loop, then break
if (swapped == false)
break;
}
}
// Function to print an array
static void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
// Driver program
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90 };
int n = arr.length;
bubbleSort(arr, n);
System.out.println("Sorted array: ");
printArray(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.
Python3
# Python3 Optimized implementation
# of Bubble sort
# An optimized version of Bubble Sort
def bubbleSort(arr):
n = len(arr)
# Traverse through all array elements
for i in range(n):
swapped = False
# Last i elements are already
# in place
for j in range(0, n-i-1):
# traverse the array from 0 to
# n-i-1. Swap if the element
# found is greater than the
# next element
if arr[j] > arr[j+1] :
arr[j], arr[j+1] = arr[j+1], arr[j]
swapped = True
# IF no two elements were swapped
# by inner loop, then break
if swapped == False:
break
# Driver code to test above
arr = [64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90]
bubbleSort(arr)
print ("Sorted array :")
for i in range(len(arr)):
print ("%d" %arr[i],end=" ")
# This code is contributed by Shreyanshi Arun
C#
// Optimized C# implementation
// of Bubble sort
using System;
class GFG
{
// An optimized version of Bubble Sort
static void bubbleSort(int []arr, int n)
{
int i, j, temp;
bool swapped;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
swapped = false;
for (j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
{
// swap arr[j] and arr[j+1]
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
swapped = true;
}
}
// IF no two elements were
// swapped by inner loop, then break
if (swapped == false)
break;
}
}
// Function to print an array
static void printArray(int []arr, int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Driver method
public static void Main()
{
int []arr = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};
int n = arr.Length;
bubbleSort(arr,n);
Console.WriteLine("Sorted array");
printArray(arr,n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007
PHP
<?php
// PHP Optimized implementation
// of Bubble sort
// An optimized version of Bubble Sort
function bubbleSort(&$arr)
{
$n = sizeof($arr);
// Traverse through all array elements
for($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
{
$swapped = False;
// Last i elements are already
// in place
for ($j = 0; $j < $n - $i - 1; $j++)
{
// traverse the array from 0 to
// n-i-1. Swap if the element
// found is greater than the
// next element
if ($arr[$j] > $arr[$j+1])
{
$t = $arr[$j];
$arr[$j] = $arr[$j+1];
$arr[$j+1] = $t;
$swapped = True;
}
}
// IF no two elements were swapped
// by inner loop, then break
if ($swapped == False)
break;
}
}
// Driver code to test above
$arr = array(64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90);
$len = sizeof($arr);
bubbleSort($arr);
echo "Sorted array :
";
for($i = 0; $i < $len; $i++)
echo $arr[$i]." ";
// This code is contributed by ChitraNayal.
?>
The end!